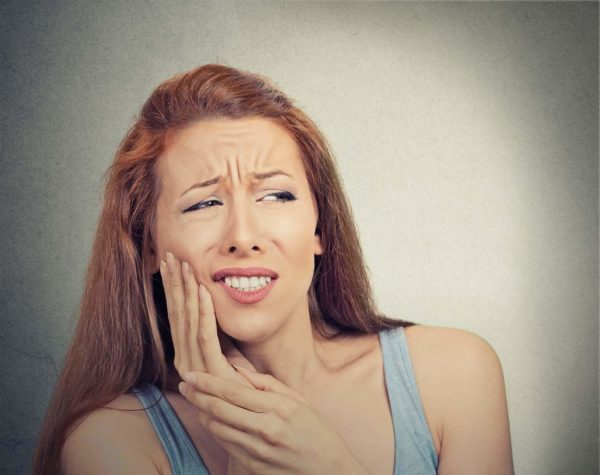
Toothache
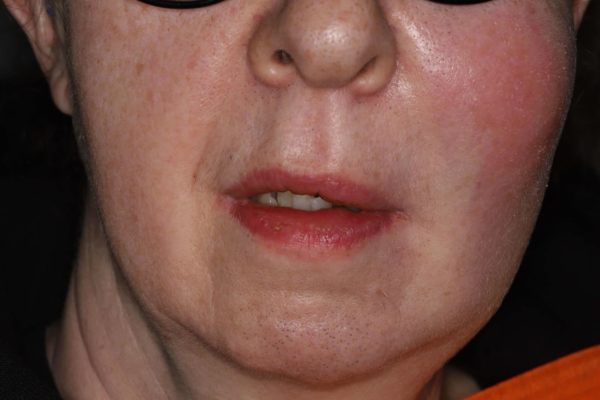
Toothache is pain in the mouth or surrounding area. The causes may be multiple, originating in the oral cavity itself (teeth, gums, tongue, etc.) or in the surrounding area (sinuses, ear, etc.).

How does a toothache manifest itself?
Sensitivity – dental pain to cold
Cold thermal stimulus usually causes pain similar to electric shocks that are usually short-lived (a few seconds or minutes) with a return to a normal state. The best thing to do is to consult a dentist
This dental hypersensitivity is explained by the absence of one of the two protective tissues of the tooth: the enamel layer and/or the gum. This absence can have many causes, such as :
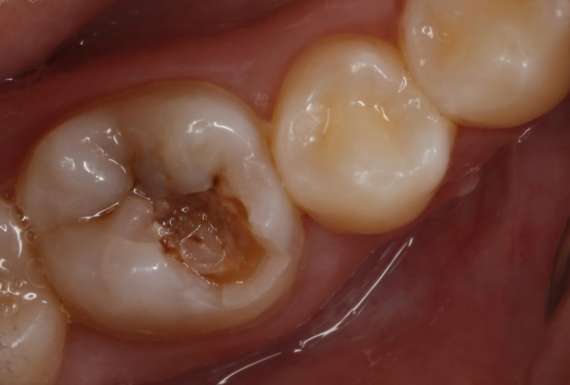
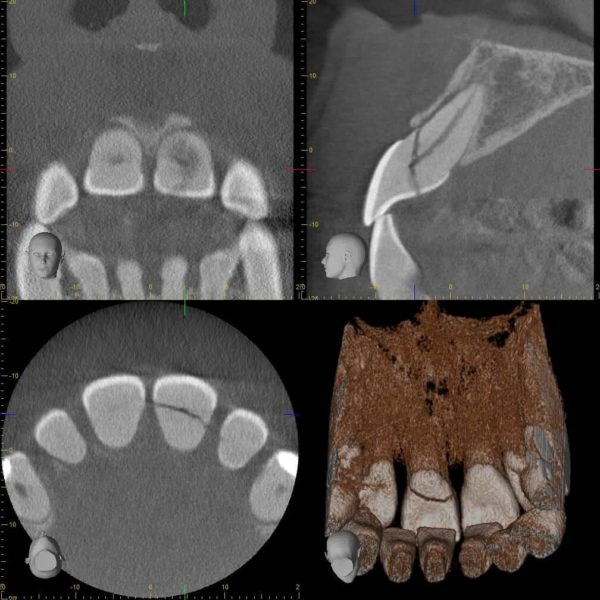
Tooth decay
It’s an infectious disease that progressively destroys the layers of the tooth from the outside in, and when it reaches the dentin, hypersensitivity can occur.
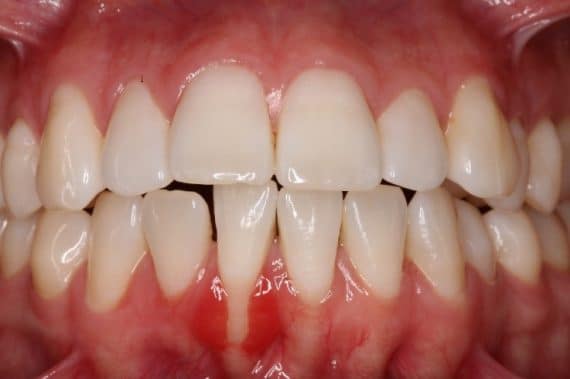
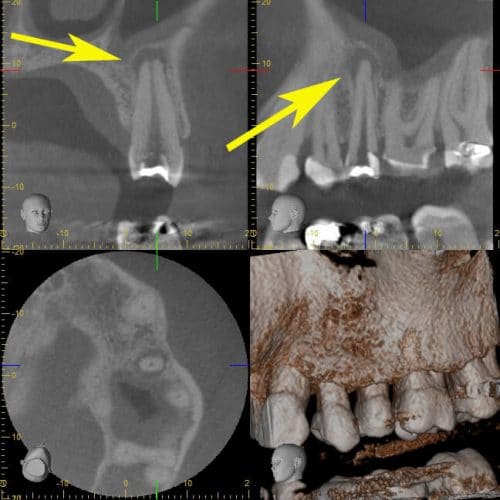
Gingival recession
This is the loss of the gums covering the roots of the teeth.
How long a toothache lasts depends on the cause of the pain and the patient’s attitude. While some pains may subside with time, others will progress to an intensity that is difficult to bear, creating a large dental abscess and sometimes requiring hospitalization.
Dental pain in the warm
When the pulp of a living tooth becomes irreversibly inflamed (at this stage, even if the cause were to be removed, the pulp inflammatory process is so advanced that it becomes irreversible leading to necrosis of the dental nerve), the tooth becomes (very) painful to hot thermal stimuli. The causes can be highly variable (caries, tooth fracture, old trauma), and root canal treatment becomes unavoidable.
The origin of permanent pain :
Pain when brushing teeth
Acute gingival necrosis (AGN)
This infection, which rapidly destroys the soft tissues supporting the teeth, is responsible for acute pain, bleeding when brushing and bad breath.
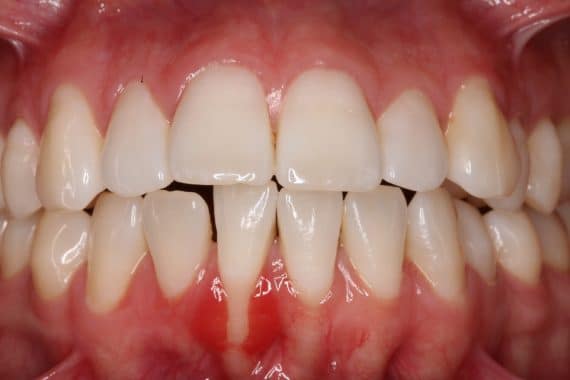
Periodontal recession
Gingival recession is characterized by the loss of gum tissue covering the root of the tooth, and the exposure of this root can cause pain on contact with toothbrush bristles.
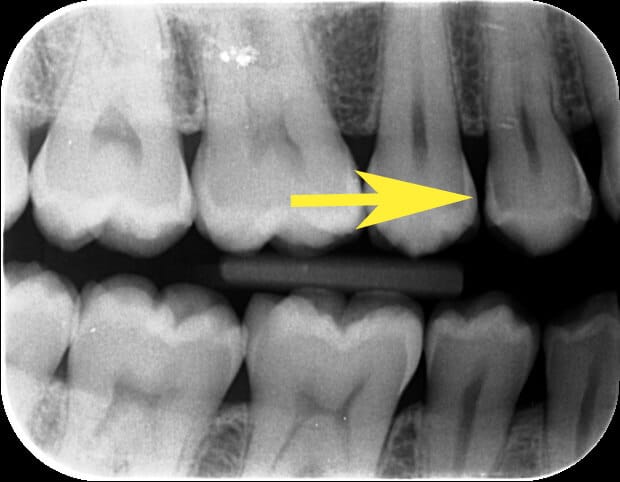
Pain during or after meals
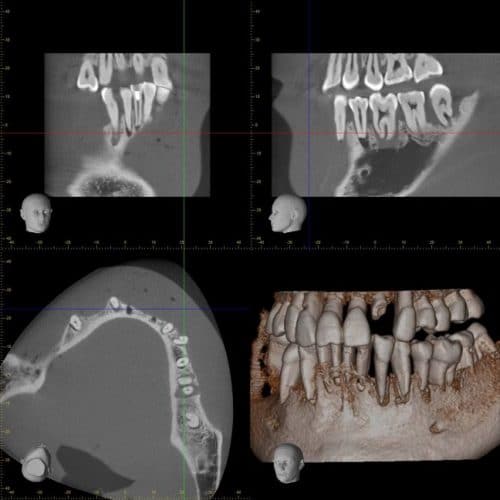
These pains correspond to a form of inflammation of the gums between the teeth, known as “septum syndrome”. They result from a combination of food compaction and bacterial growth, leading to inflammation of the interdental region.
Tooth pain or toothache is often the first sign of a malfunctioning chewing apparatus. If you ignore tooth pain, more extensive and consequential damage can occur in other areas of the oral cavity.
Teeth play a vital role in digestive function, and it’s unfortunate to have to extract several teeth out of neglect for dental pain.